This Is How Our Brain Works
The activities of the nervous system are concentrated in the brain. Although the different parts of the brain are interconnected, the functions of the brain are divided into different areas.
The brain is a complex organ and extremely important. As we know, it controls various actions of the body as well as our feelings, thoughts and memories.
It is quite normal for us to forget some of its functions and not remember every single component, as this is not part of our everyday life (except for neurologists or neuroscientists). To make things a little easier for you, we are going to introduce you to the structure and function of our brain.
The brain is made up of a large number of neurons. These are nerve cells that receive, process and transmit information via bioelectrical impulses. However, it is still unclear how powerful it really is. For this reason, scientists continue to research this organ and its dimensions. Fascinating, isn’t it?
The brain, a vital organ
The brain weighs around 1.36 kilograms, with the cerebellum making up the largest part of the weight, namely around 85%. However, so that its weight does not make it difficult for people to move, the brain swims in the liquor within a bone structure, the skull.
The brain consists of 78% water, 10% fat and 8% protein. It only makes up about 2% of our total body weight and uses 20% of the energy we produce. It is divided into the following areas:
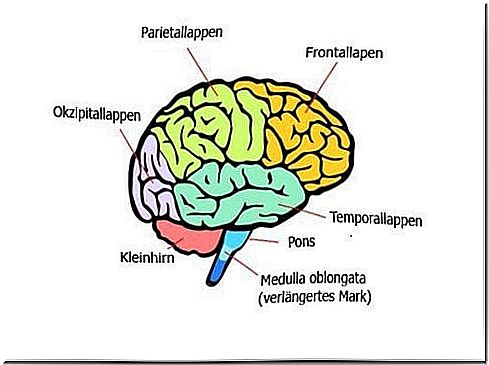
1. brain stem
The brain stem is located at the base of the skull and controls vital functions such as heart rate, digestion, breathing and blood pressure. It also connects the brain to the rest of the body through the spinal cord. The brain stem is divided into the mesencephalon, pons and medulla oblongata (elongated medulla).
2. cerebellum
The cerebellum is responsible for maintaining balance, maintaining muscle tension and coordinating body movements. It ensures that our movements are coordinated and executed precisely.
3. cerebrum
The cerebrum is related to our feelings, emotions, memories and reactions. In short, as the head of our consciousness and memory, it receives and processes signals and stimuli and gives an appropriate response. For example, when you place your hand on a hot surface, your brain receives a signal that the temperature is too high and responds by sending a command to the muscles in your hand to remove them immediately.
Other important brain structures
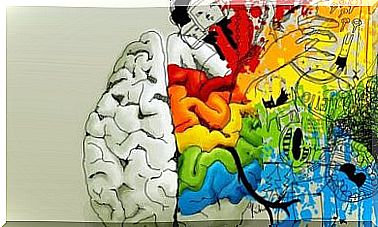
Left and right hemispheres of the brain
The cerebral cortex is a thin and wrinkled layer. The brain is divided into two halves, the left and the right, which in turn are divided into 4 lobes.
The right hemisphere is responsible for non-verbal expression. For example, intuition and the recognition of faces, voices, melodies, etc. In this hemisphere, thoughts and memories manifest themselves in the form of images.
If the left hemisphere is damaged, people have problems speaking and writing, but also with expressing themselves or understanding language. Functions such as the ability to analyze, logical conclusions and understanding of numbers are located there.
Today, however, the two halves are believed to work together so that many functions are performed by both sides.
The two halves of the brain are connected by the corpus callosum. The right hemisphere is responsible for controlling the left half of the body, while the left hemisphere is in control of the right half of the body.
Cerebral lobe
Each half of the brain is divided into 4 lobes:
- Frontal lobes: this is where our conscious thinking is processed and problem solutions take place.
- Parietal lobe: is responsible for the perception of stimuli in connection with the sense of touch, pressure, temperature and pain.
- Temporal lobe: is responsible for the perception and recognition of auditory stimuli as well as memory.
- Occipital lobe: visual stimuli.
Conclusion
The brain is an incredibly powerful and complex organ. It controls all aspects of our life, including some that we are not even aware of (like breathing). It also affects our conscious movements. And even if the functions of our brain still raise many questions, the latest research always delivers new, interesting results.