T-DM1 In Cancer Treatment: What Is It?
Around 18 to 20 percent of women with breast cancer suffer from the HER2-positive metastatic type, which means that the HER2 receptor is produced in excess. A new medicine known as T-DM1 has been developed for this type of breast cancer. Find out more about this topic today.
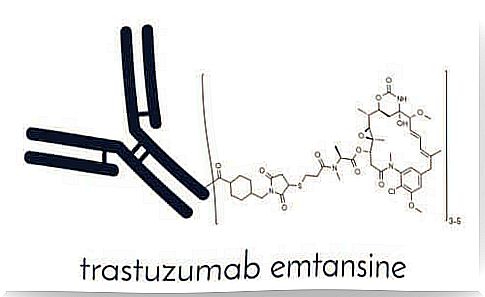
T-DM1 is a new, unique and selectively proven drug conjugate that has been approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of advanced HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.
HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2) is a protein that promotes the growth of cancer cells. The drug is marketed under the name Kadcyla .
T-DM1 consists of two active substances: One component is the well-known drug trastuzumab, an antibody against HER2 / neu. This is conjugated with the cytotoxic microtubule inhibitor DM1. This means that DM1 has the ability to block the synthesis of microtubules in cell division. We will take a closer look at this mechanism later.
T-DM1: Efficiency in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer

Around 18 to 20 percent of women with breast cancer suffer from the HER2-positive metastatic type, which means that the HER2 receptor is produced in excess. Before specific anti-HER2 therapies against this oncogene were developed, the prognosis for patients with HER2-positive tumors was worse than for other breast cancers.
Fortunately, however, the development of trastuzumab, a drug approved in 2000, has significantly improved the prognosis of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. In 2014, a second anti-HER2 drug came onto the market: pertuzumab. First-line treatment of advanced HER-2 breast cancer with this medicine may improve the chances of survival.
To date, only a combination of chemotherapy with capecitabine and lapatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of HER2 / ERGFR, has been recognized as a second-line treatment for advanced HER2-positive breast cancer .
A registry study called EMILIA compared treatment with T-DM1 with lapatinib and capecitabine in patients with this type of breast cancer who had previously been treated with a combination of trastuzumab and taxanes.
The results of this study showed that affected patients lived longer, the progression of the disease could be delayed, and side effects could be better tolerated. In addition, the symptoms could be delayed significantly with treatment with T-DM1.
Mechanism of action: What does T-DM1 do in the organism?
As mentioned earlier, T-DM1 is a combination of two drugs: trastuzumab and DM1. So T-DM1 combines the mechanisms of action of these two drugs:
- Like trastuzumab, T-DM1 is able to bind to HER2 / neu receptors and block the growth of tumor cells by inhibiting intrecellular signaling.
- In addition, the mechanism of action of the cytostatic drug DM1 enables it to bind to tubulin.
Inhibiting tubulin prevents the cancer cell from dividing, which ultimately leads to its death through apoptosis. The results of the in vitro cytotoxicity tests showed that DM1 is between 20 and 200 times more potent than taxanes and vinca alkaloids.
Side effects of T-DM1
Side effects are all those effects of a drug that are not wanted or intended, but occur in the context of pharmacological treatment.
The most common reports of nausea, fatigue, and headache were reported by patients treated with this drug. This affected ≥25 percent. With this in mind, the safety of T-DM1 was tested in a total of 1,871 patients with breast cancer in various clinical trials, with the following side effects being the most common:
- Bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Bone and muscle pain
- stomach pain
- Thrombocytopenia
- Vomit
Conclusion
The data resulting from studies have shown that T-DM1 is a significant improvement in the treatment of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer. This can extend the life of patients previously treated with trastuzumab.
Despite these advances, metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer remains incurable. So it is necessary to find new and more efficient therapies that are better tolerated. Therefore, active research on breast cancer is of the utmost importance.