Hearing Impairment: Symptoms And Treatment
Around 360 million people worldwide suffer from hearing loss. The likelihood of developing it increases with age. Find out more about this topic today.

Hearing impairment or hypacusis refers to a reduction in hearing, which often has a severe impact on everyday life. Before we get into this disorder, let’s take a quick look at how hearing works.
The sound penetrates through the air to the ear, is picked up by the auricle and then reaches the ear. The eardrum then converts the sound into vibrations, which are transmitted to the inner ear via the ossicles.
There the hair cells are set in motion to enable the transmission of the sensory stimulus to the brain. The auditory nerve is responsible for this. The nerve signals are then processed in the brain. This process enables us to hear.
Depending on where exactly the hearing process is disturbed, there are different types of hearing loss . Find out more about it afterwards.
Different types of hearing loss
Basically, there are two types of hypacusis: conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss.
In the case of conductive hearing loss, the transmission of the sound is hindered if, for example, the outer or middle ear (especially the eardrum or ossicles) is damaged. Sensorineural hearing loss is a problem in the inner ear or brain (cochlea, auditory nerve, brain stem, or cerebral cortex).
Symptoms of hearing loss
This disease is usually recognized late. This is due to the fact that the organism automatically develops balancing strategies. There are a wide range of changes that are often associated with hypacusis.
The most obvious symptom is hearing loss. In the case of conductive hearing loss, it is difficult to distinguish between low-intensity sounds. If you have sensorineural hearing loss, however, it is more difficult to distinguish between the sounds, even if you can hear their intensity.

If you are hard of hearing, it is usually difficult to hear high tones. Therefore it is usually easier to hear male voices than female. In noisy environments it is also difficult to distinguish different sounds from one another, and some sounds can be heard more than they actually are.
Depending on the cause, there are also various other symptoms: the most common include earache, in the case of otitis stabbing, throbbing pain with a feeling of pressure. If the balance organ in the ear is damaged, dizziness can also occur.
An acute hearing loss that is not treated makes communication difficult. This in turn can have psychological consequences and have a negative effect on the state of mind (e.g. through depression).
Treatment of hearing loss
In order to choose the right treatment, it is first necessary to diagnose the causes. Depending on the type, the doctor will then recommend one or the other therapy.
Conductive hearing loss
If the build-up of wax makes hearing difficult, the solution is simple: the doctor will professionally clean the ears. However, if the ossicular chain defects are present, tympanoplasty (surgery) may be considered to heal or replace them.
Antibiotics are given for an otitis media. If there is fluid in the ear (e.g. due to a previous infection), it must be removed.
If the eardrum is injured (tympanic membrane perforation), or if there is a scar from a previous injury or infection, a tympanoplasty may also be necessary to close or replace the eardrum.
Another possibility is an implanted hearing aid that picks up the sound and transmits it to the inner ear. Problems with sound transmission in the outer or middle ear can also be solved in this way.
Sensorineural hearing loss
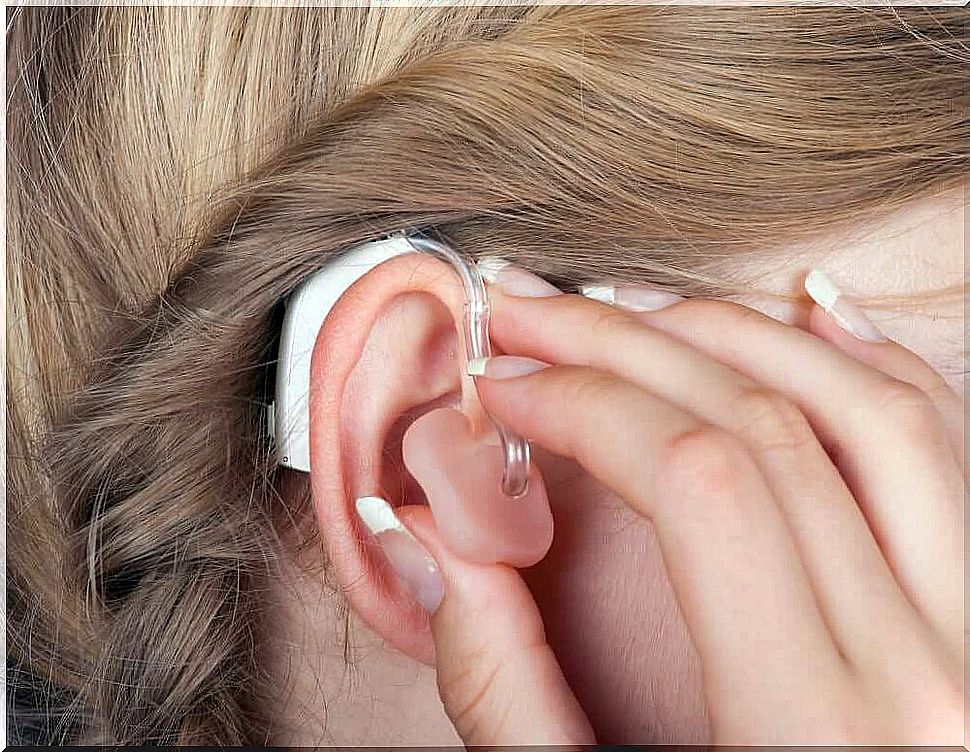
In these cases, there is usually no solution that can reverse the hearing loss. You then need an implant that can take over the neurosensory functions. A hearing aid is also a good way to (at least partially) compensate for the loss of perception.
There are two basic types of implants:
- Cochlear implant: electronic hearing prosthesis that replaces the function of the inner ear.
- Brain stem implant or central auditory implant: electronic device that stimulates this area of the brain directly without the sound having to be transmitted from the inner ear or the auditory nerve.
The specialist examination is essential in order to initiate the correct treatment.