The Properties And Benefits Of Betaine
Betaine is a natural nutrient that performs important tasks in cooperation with various organs. At the same time, it prevents heart, muscle and digestive diseases.

Has your doctor already explained the properties and benefits of betaine to you? Sometimes our doctors advise specific nutrients that our bodies need to function properly. At the same time, they also recommend us to adopt certain habits or eating habits to avoid health problems.
And then in those conversations things like “betaine” and ” benefits of betaine ” come up. However, we often only understand half of what they tell us. It is therefore worth reading the following article at this point to learn more about the benefits of betaine. We also explain what betaine does in our body.
What is betaine?
Betaine is a naturally occurring compound. It provides hydrochloric acid and is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12, calcium and iron.
It is essentially a nutrient that distributes methyl groups in the body. In the case of destabilizing risks, any organ can use these methyl groups.
Foods rich in betaine
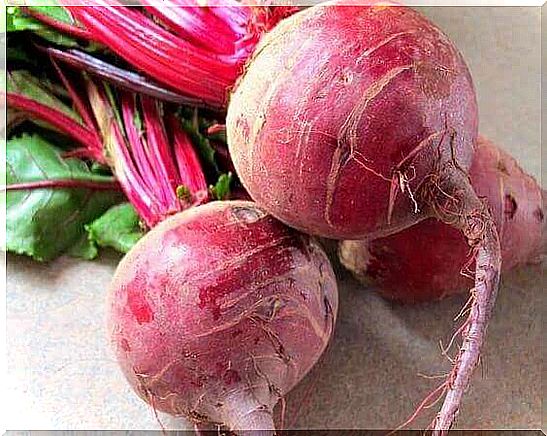

Beets (or beets) are one of the greatest sources of betaine. The name of this vegetable is derived from the betaine it contains.
Other foods rich in betaine:
- fish
- spinach
- broccoli
- Vegetables in general
What does betaine do?
It can be difficult to understand how betaine works. Therefore, here are a few points that summarize this:
Regulates homocysteine
Betaine helps regulate and reduce homocysteine levels. It is also responsible for preventing diseases caused by too much homocysteine in your body.
Although homocysteine is necessary, it still needs to be regulated so that it does not cause problems.
If there is too much of it in your body, it can lead to the following problems:
- Heart attacks
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Blood clots
- Strokes
Keeps your liver healthy
This amino acid acts as a lipotropic agent in delivering methyl compounds to break down fats and release the liver.
This prevents the fatty liver. In some cases, betaine is also used to treat the diseased organ.
Other functions of betaine:
- Aids digestion by providing hydrochloric acid, which is needed in the stomach to break down proteins.
- Prevents the cells from drying out by maintaining the water balance. Participation in the transport of fluids that are needed throughout the body.
- It is involved in creatine synthesis and strengthens muscle building.
Benefits of betaine
Each of the above functions is directly linked to a number of health benefits. A person who ingests a reasonable percentage of this nutrient will:
- Have a lower risk of gastrointestinal disease. Have a regulated acidity, which is necessary for good digestion.
- Have less fat, which means the liver stays healthy. Fight excess fat around the liver.
- Have healthier arteries and a healthier cardiovascular system because of the methyls. Have free flowing blood.
- Have more muscle endurance and strength. Because there is a greater amount of nitric oxide, it leads to more strength for physical activity.
Many top athletes use supplements of this nutrient. Betaine also helps with many body functions.
As you have already learned in our post, betaine is necessary and relevant for your everyday life. It also helps to avoid future discomfort.
You can also buy betaine as a supplement. And in this way supplement the proportion of betaine that occurs naturally and is absorbed through foods that contain it.
Note, however, that the dosage varies from person to person. Therefore, every patient should follow their doctor’s advice to avoid side effects.
Side effects of betaine supplementation

Some experts prescribe drugs containing betaine to treat various health problems.
However, as with all chemicals, there are side effects that you should be aware of. Therefore, if you have the following side effects, visit a hospital or your doctor:
- nausea
- Changes in your body odor
- Faint
- Muscle weakness
- Visual distortion
- Memory problems
- Motor difficulties
Some facilities have announced that patients treated with betaine have had cases of cerebral edema. It is therefore advisable to stop taking it and have the appropriate tests carried out.
Betaine production declines from around the age of 50. Educating and including foods rich in betaine in your diet will help maintain organic balance.
You can also visit a hospital to analyze betaine chemical uptake.