Papilla Or Papilla Edema: What Is It?
The papillae leads to blurred or double vision and can also lead to temporary graying of the field of vision. Today we explain to you how this swelling of the papilla occurs, which is associated with increased intracranial pressure.
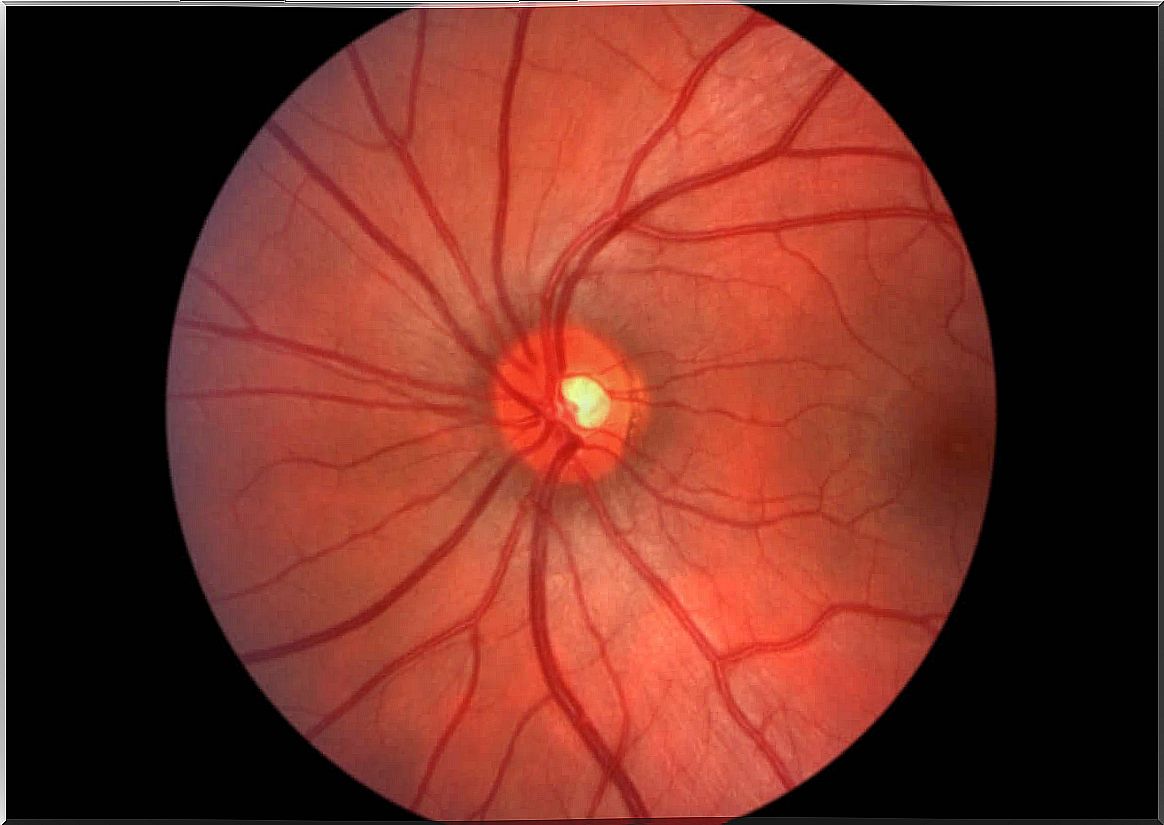
The congestive papilla or papillary edema is a disease of the eye in which the optic nerve becomes inflamed at the transition to the retina. This is due to increased intracranial pressure.
This disease can be asymptomatic or it can cause various visual problems. The problem, however, is that this edema at the confluence of the optic nerve with the retina can hide serious diseases. For example, it could be an indication of a brain tumor. Learn more about this topic in our article today.
What is a papillae?
As already mentioned, the congestive papilla can be recognized by a swelling or bulging of the optic nerve head. In most cases, this problem occurs on both sides, which is then referred to as bilateral edema.
The reason for this is increased intracranial pressure, which can be attributed to various causes. The skull is a bone structure that protects various organs and substances, including the cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid. When there is swelling within the skull, the pressure increases.
A congestive papilla occurs when the intracranial pressure is too high, for example due to a brain tumor. But there could also be other reasons.
Possible causes of a congestive papilla
We have already pointed out that the increased intracranial pressure can be the trigger for congestive papillae. It can be caused by tumors, abscesses caused by an infection, or bleeding.
A study published in the journal Neurología Suplementos indicates that diopathic intracranial hypertension could also be the cause of papillae congestion. This means that the reason for the increased intracranial pressure is not always known.
In other cases, menigitis or encephalitis leads to papilledema. An article in the Acta Neurológica Colombiana confirms that it could also be a symptom of Wernicke’s disease. Other possible causes are:
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- Hypervitaminosis A.
- Tumor in the spinal cord
- Upper Influence Damming (OES)
What symptoms does a congestive pulp cause?
The symptoms of this disease are variable. At first it can be asymptomatic, which means that the injury can only be seen by looking at the fundus of the eye. But once the fibers of the optic nerve are damaged, the symptoms are obvious.
They manifest themselves through various visual disturbances: Those affected often suffer from blurred or double vision. In addition, the field of vision can also be temporarily gray, causing brief vision loss that can last a few seconds. The increased intracranial pressure also leads to specific complaints such as headache, nausea and vomiting.
The headache is worse in the morning after waking up than during the day. If the causative disease is meningitis, stiffness in the neck area can also occur.
How do you treat papillary edema?
The most important thing in treating papillary congestion is to reduce intracranial pressure to a normal level. It must be taken into account that it is a medical emergency. When idiopathic intracranial hypertension is present, doctors solve the problem by reducing cerebrospinal fluid.
The journal Revista Chilena de Neurocirugia explains that diuretics such as mannitol or furosemide can be used in this case. Weight reduction can also be beneficial. In addition, those affected should reduce salt and fluid consumption.
In order for the cerebrospinal fluid to circulate properly, it is also advisable to raise your head slightly when sleeping. If none of these measures help, surgery may be necessary.
The doctor performs a lumbar puncture to remove some of the cerebrospinal fluid. If an infection is the cause of the papillae, the treating doctor will give antibiotics. This is also the case if there is an abscess caused by bacteria.
Final summary
A congestive papilla occurs when there is a swelling or bulging of the optic nerve head due to increased intracranial pressure. Various causes can trigger this problem, but in very many cases there is idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Furthermore, diseases such as a brain tumor, bleeding or infections can lead to it. Disc edema is a medical emergency that requires urgent treatment to avoid irreversible damage.